When choosing a database for your application, you need ask yourself many questions and there are important rules about Data Architecture
- there’s no standard solution that fits all
- the business and it’s data defines the architecture
- you need to find the right tool that does job
- you can use multiple databases, different types depending on the characteristics of each data subset
It is very important to decide carefully, after your application grown it could be very difficult to change. The CAP theorem, also known as Brewer’s theorem, states that it is impossible for a distributed computer system to simultaneously provide all three of the following guarantees:
- Consistency (all nodes see the same data at the same time)
- Availability (a guarantee that every request receives a response about whether it was successful or failed)
- Partition tolerance (the system continues to operate despite arbitrary message loss or failure of part of the system)
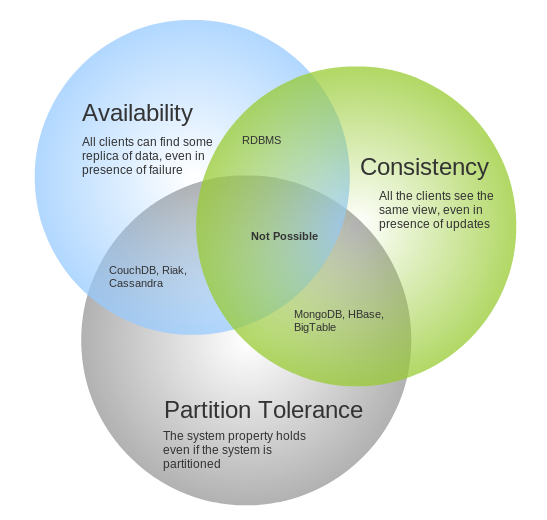
Once you have defined which of those guarantees is less important for your app and can be sacrificed, you have a smaller subset of options to choose from. However this not the only thing you need to consider, you may want to use a specific framework such as Hibernate, Spring, Django or WordPress, and take advantage of the of-the-shelf capabilities, in that case you want to use a SQL database.
Other questions that will help you decide which database works best:
- What is the data like? What's the nature of it?
- How is the data updated?
- How is the data read?
- Do you need limited access permissions?
- How important is documentation and community support?
Micah Yoder explains it very well in this video
Data Architecture is not just about choosing the right data store, other aspects to analyze are:
- Low Cost ( preferably open source, no hidden costs… )
- Simple to Implement and Scale
- Learning Curve
- Rapid Development
- Operational Maintenance
- Ability to Do Online Changes